Acupuncture: What You Need To Know
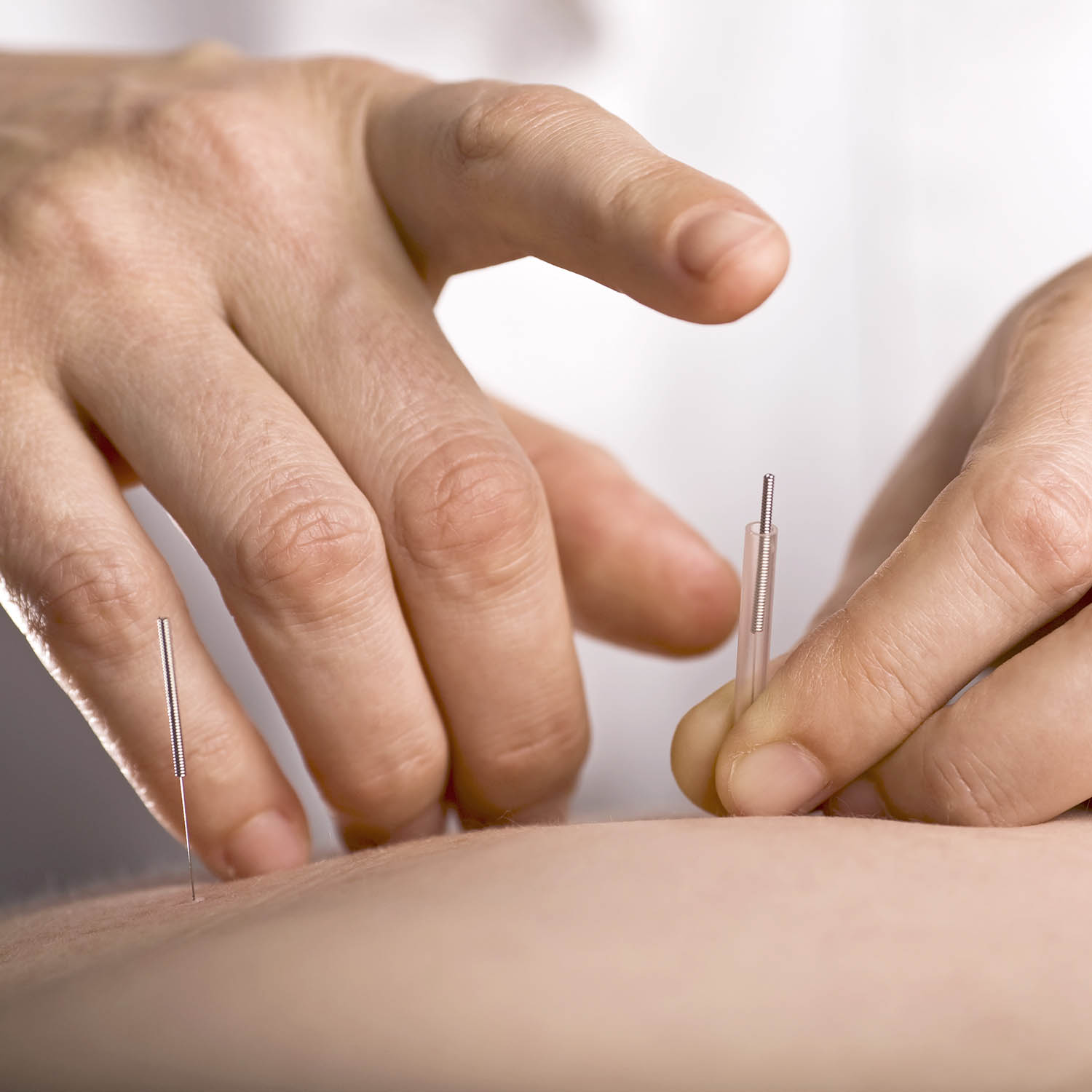
What is acupuncture?
Acupuncture is a technique in which practitioners insert fine needles into the skin to treat health problems. The needles may be manipulated manually or stimulated with small electrical currents (electroacupuncture). Acupuncture has been in use in some form for at least 2,500 years. It originated from traditional Chinese medicine but has gained popularity worldwide since the 1970s.
How widely is acupuncture used?
According to the World Health Organization, acupuncture is used in 103 of 129 countries that reported data.
In the United States, data from the National Health Interview Survey showed a 50 percent increase in the number of acupuncture users between 2002 and 2012. In 2012, the most recent year for which statistics are available, 6.4 percent of U.S. adults reported they had used acupuncture, and 1.7 percent reported they had used it in the past 12 months.
What is acupuncture used for?
National survey data indicate that in the United States, acupuncture is most commonly used for pain, such as back, joint, or neck pain.
How does acupuncture work scientifically?
How acupuncture works is not fully understood. However, there’s evidence that acupuncture may have effects on the nervous system, effects on other body tissues, and nonspecific (placebo) effects.
- Studies in animals and people, including studies that used imaging methods to see what’s happening in the brain, have shown that acupuncture may affect nervous system function.
- Acupuncture may have direct effects on the tissues where the needles are inserted. This type of effect has been seen in connective tissue.
- Acupuncture has nonspecific effects (effects due to incidental aspects of a treatment rather than its main mechanism of action). Nonspecific effects may be due to the patient’s belief in the treatment, the relationship between the practitioner and the patient, or other factors not directly caused by the insertion of needles. In many studies, the benefit of acupuncture has been greater when it was compared with no treatment than when it was compared with sham (simulated or fake) acupuncture procedures, such as the use of a device that pokes the skin but does not penetrate it. These findings suggest that nonspecific effects contribute to the beneficial effect of acupuncture on pain or other symptoms.
- In recent research, a nonspecific effect was demonstrated in a unique way: Patients who had experienced pain relief during a previous acupuncture session were shown a video of that session and asked to imagine the treatment happening again. This video-guided imagery technique had a significant pain-relieving effect.
What does research show about the effectiveness of acupuncture for pain?
Research has shown that acupuncture may be helpful for several pain conditions, including back or neck pain, knee pain associated with osteoarthritis, and postoperative pain. It may also help relieve joint pain associated with the use of aromatase inhibitors, which are drugs used in people with breast cancer.
An analysis of data from 20 studies (6,376 participants) of people with painful conditions (back pain, osteoarthritis, neck pain, or headaches) showed that the beneficial effects of acupuncture continued for a year after the end of treatment for all conditions except neck pain.
Back or Neck Pain
- In a 2018 review, data from 12 studies (8,003 participants) showed acupuncture was more effective than no treatment for back or neck pain, and data from 10 studies (1,963 participants) showed acupuncture was more effective than sham acupuncture. The difference between acupuncture and no treatment was greater than the difference between acupuncture and sham acupuncture. The pain-relieving effect of acupuncture was comparable to that of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
- A 2017 clinical practice guideline from the American College of Physicians included acupuncture among the nondrug options recommended as first-line treatment for chronic low-back pain. Acupuncture is also one of the treatment options recommended for acute low-back pain. The evidence favoring acupuncture for acute low-back pain was judged to be of low quality, and the evidence for chronic low-back pain was judged to be of moderate quality.
For more information, see the NCCIH webpage on low-back pain.
Osteoarthritis
- In a 2018 review, data from 10 studies (2,413 participants) showed acupuncture was more effective than no treatment for osteoarthritis pain, and data from 9 studies (2,376 participants) showed acupuncture was more effective than sham acupuncture. The difference between acupuncture and no treatment was greater than the difference between acupuncture and sham acupuncture. Most of the participants in these studies had knee osteoarthritis, but some had hip osteoarthritis. The pain-relieving effect of acupuncture was comparable to that of NSAIDs.
- A 2018 review evaluated 6 studies (413 participants) of acupuncture for hip osteoarthritis. Two of the studies compared acupuncture with sham acupuncture and found little or no difference between them in terms of effects on pain. The other four studies compared acupuncture with a variety of other treatments and could not easily be compared with one another. However, one of the trials indicated that the addition of acupuncture to routine care by a physician may improve pain and function in patients with hip osteoarthritis.
- A 2019 clinical practice guideline from the American College of Rheumatology and the Arthritis Foundation conditionally recommends acupuncture for osteoarthritis of the knee, hip, or hand. The guideline states that the greatest number of studies showing benefits have been for knee osteoarthritis.
For more information, see the NCCIH webpage on osteoarthritis.
Headache and Migraine
- A 2020 review of nine studies that compared acupuncture with various drugs for preventing migraine found that acupuncture was slightly more effective, and study participants who received acupuncture were much less likely than those receiving drugs to drop out of studies because of side effects.
- There’s moderate-quality evidence that acupuncture may reduce the frequency of migraines (from a 2016 evaluation of 22 studies with almost 5,000 people). The evidence from these studies also suggests that acupuncture may be better than sham acupuncture, but the difference is small. There is moderate- to low-quality evidence that acupuncture may reduce the frequency of tension headaches (from a 2016 evaluation of 12 studies with about 2,350 people).
For more information, see the NCCIH webpage on headache.
Myofascial Pain Syndrome
- Myofascial pain syndrome is a common form of pain derived from muscles and their related connective tissue (fascia). It involves tender nodules called “trigger points.” Pressing on these nodules reproduces the patient’s pattern of pain.
- A combined analysis of a small number of studies of acupuncture for myofascial pain syndrome showed that acupuncture applied to trigger points had a favorable effect on pain intensity (5 studies, 215 participants), but acupuncture applied to traditional acupuncture points did not (4 studies, 80 participants).
Sciatica
- Sciatica involves pain, weakness, numbness, or tingling in the leg, usually on one side of the body, caused by damage to or pressure on the sciatic nerve—a nerve that starts in the lower back and runs down the back of each leg.
- Two 2015 evaluations of the evidence, one including 12 studies with 1,842 total participants and the other including 11 studies with 962 total participants, concluded that acupuncture may be helpful for sciatica pain, but the quality of the research is not good enough to allow definite conclusions to be reached.
Postoperative Pain
- A 2016 evaluation of 11 studies of pain after surgery (with a total of 682 participants) found that patients treated with acupuncture or related techniques 1 day after surgery had less pain and used less opioid pain medicine after the operation.
Cancer Pain
- A 2016 review of 20 studies (1,639 participants) indicated that acupuncture was not more effective in relieving cancer pain than conventional drug therapy. However, there was some evidence that acupuncture plus drug therapy might be better than drug therapy alone.
- A group of drugs called aromatase inhibitors has been shown to be of value in treating hormone-sensitive breast cancer, but the drugs can cause joint pain and stiffness, and patients sometimes stop taking them because of these side effects. Acupuncture has been studied to see whether it is helpful for this type of pain.
- A 2017 review of 5 studies (181 participants) of acupuncture for aromatase inhibitor-induced joint pain in breast cancer patients concluded that 6 to 8 weeks of acupuncture treatment may help reduce the pain. However, the individual studies only included small numbers of women and used a variety of acupuncture techniques and measurement methods, so they were difficult to compare.
- A larger 2018 study included 226 women with early-stage breast cancer who were taking aromatase inhibitors. The study found that the women who received 6 weeks of acupuncture treatment, given twice each week, reported less joint pain than the participants who received sham or no acupuncture.
Chronic Prostatitis/Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome
- Chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome is a condition in men that involves inflammation of or near the prostate gland; its cause is uncertain.
- A review of 3 studies (204 total participants) suggested that acupuncture may reduce prostatitis symptoms, compared with a sham procedure. Because follow-up of the study participants was relatively brief and the numbers of studies and participants were small, a definite conclusion cannot be reached about acupuncture’s effects.
Irritable Bowel Syndrome
- A 2019 review of 41 studies (3,440 participants) showed that acupuncture was no more effective than sham acupuncture for symptoms of irritable bowel syndrome, but there was some evidence that acupuncture could be helpful when used in addition to other forms of treatment.
For more information, see the NCCIH webpage on irritable bowel syndrome.
Fibromyalgia
- A 2019 review of 12 studies (824 participants) of people with fibromyalgia indicated that acupuncture was significantly better than sham acupuncture for relieving pain, but the evidence was of low-to-moderate quality.
For more information, see the NCCIH webpage on fibromyalgia.
What does research show about acupuncture for conditions other than pain?
In addition to pain conditions, acupuncture has also been studied for at least 50 other health problems. There is evidence that acupuncture may help relieve seasonal allergy symptoms, stress incontinence in women, and nausea and vomiting associated with cancer treatment. It may also help relieve symptoms and improve the quality of life in people with asthma, but it has not been shown to improve lung function.
Seasonal Allergies (Allergic Rhinitis or Hay Fever)
- A 2015 evaluation of 13 studies of acupuncture for allergic rhinitis, involving a total of 2,365 participants, found evidence that acupuncture may help relieve nasal symptoms. The study participants who received acupuncture also had lower medication scores (meaning that they used less medication to treat their symptoms) and lower blood levels of immunoglobulin E (IgE), a type of antibody associated with allergies.
- A 2014 clinical practice guideline from the American Academy of Otolaryngology–Head and Neck Surgery included acupuncture among the options health care providers may offer to patients with allergic rhinitis.
For more information, see the NCCIH webpage on seasonal allergies.
Urinary Incontinence
- Stress incontinence is a bladder control problem in which movement—coughing, sneezing, laughing, or physical activity—puts pressure on the bladder and causes urine to leak.
- In a 2017 study of about 500 women with stress incontinence, participants who received electroacupuncture treatment (18 sessions over 6 weeks) had reduced urine leakage, with about two-thirds of the women having a decrease in leakage of 50 percent or more. This was a rigorous study that met current standards for avoiding bias.
Asthma
- In a study conducted in Germany in 2017, 357 participants receiving routine asthma care were randomly assigned to receive or not receive acupuncture, and an additional 1,088 people who received acupuncture for asthma were also studied. Adding acupuncture to routine care was associated with better quality of life compared to routine care alone.
- A review of 9 earlier studies (777 participants) showed that adding acupuncture to conventional asthma treatment improved symptoms but not lung function.
For more information, see the NCCIH webpage on asthma.
Depression
- A 2018 review of 64 studies (7,104 participants) of acupuncture for depression indicated that acupuncture may result in a moderate reduction in the severity of depression when compared with treatment as usual or no treatment. However, these findings should be interpreted with caution because most of the studies were of low or very low quality.
For more information, see the NCCIH webpage on depression.
Quitting Smoking
- In recommendations on smoking cessation treatment issued in 2021, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force, a panel of experts that makes evidence-based recommendations about disease prevention, did not make a recommendation about the use of acupuncture as a stop-smoking treatment because only limited evidence was available. This decision was based on a 2014 review of 9 studies (1,892 participants) that looked at the effect of acupuncture on smoking cessation results for 6 months or more and found no significant benefit. Some studies included in that review showed evidence of a possible small benefit of acupuncture on quitting smoking for shorter periods of time.
For more information, see the NCCIH webpage on quitting smoking.
Infertility
- A 2021 review evaluated 6 studies (2,507 participants) that compared the effects of acupuncture versus sham acupuncture on the success of in vitro fertilization as a treatment for infertility. No difference was found between the acupuncture and sham acupuncture groups in rates of pregnancy or live birth.
- A 2020 review evaluated 12 studies (1,088 participants) on the use of acupuncture to improve sperm quality in men who had low sperm numbers and low sperm motility. The reviewers concluded that the evidence was inadequate for firm conclusions to be drawn because of the varied design of the studies and the poor quality of some of them.
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- A 2018 review of 12 studies with 869 participants concluded that acupuncture and laser acupuncture (a treatment that uses lasers instead of needles) may have little or no effect on carpal tunnel syndrome symptoms in comparison with sham acupuncture. It’s uncertain how the effects of acupuncture compare with those of other treatments for this condition.
- In a 2017 study not included in the review described above, 80 participants with carpal tunnel syndrome were randomly assigned to one of three interventions: (1) electroacupuncture to the more affected hand; (2) electroacupuncture at “distal” body sites, near the ankle opposite to the more affected hand; and (3) local sham electroacupuncture using nonpenetrating placebo needles. All three interventions reduced symptom severity, but local and distal acupuncture were better than sham acupuncture at producing desirable changes in the wrist and the brain.
Hot Flashes Associated With Menopause
- A 2018 review of studies of acupuncture for vasomotor symptoms associated with menopause (hot flashes and related symptoms such as night sweats) analyzed combined evidence from an earlier review of 15 studies (1,127 participants) and 4 newer studies (696 additional participants). The analysis showed that acupuncture was better than no acupuncture at reducing the frequency and severity of symptoms. However, acupuncture was not shown to be better than sham acupuncture.
For more information, see the NCCIH webpage on menopause.
What is auricular acupuncture good for?
- Auricular acupuncture is a type of acupuncture that involves stimulating specific areas of the ear.
- Research on auricular acupuncture for chronic back pain and cancer pain has had promising results.
- In a 2019 review of 15 studies (930 participants) of auricular acupuncture or auricular acupressure (a form of auricular therapy that does not involve penetration with needles), the treatment significantly reduced pain intensity, and 80 percent of the individual studies showed favorable effects on various measures related to pain.
- A 2020 review of 9 studies (783 participants) of auricular acupuncture for cancer pain showed that auricular acupuncture produced better pain relief than sham auricular acupuncture. Also, pain relief was better with a combination of auricular acupuncture and drug therapy than with drug therapy alone.
- An inexpensive, easily learned form of auricular acupuncture called “battlefield acupuncture” has been used by the U.S. Department of Defense and Department of Veterans Affairs to treat pain. However, a 2021 review of 9 studies (692 participants) of battlefield acupuncture for pain in adults did not find any significant improvement in pain when this technique was compared with no treatment, usual care, delayed treatment, or sham battlefield acupuncture.
Is acupuncture safe?
- Relatively few complications from using acupuncture have been reported. However, complications have resulted from use of nonsterile needles and improper delivery of treatments.
- When not delivered properly, acupuncture can cause serious adverse effects, including infections, punctured organs, and injury to the central nervous system.
- The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates acupuncture needles as medical devices and requires that they be sterile and labeled for single use only.
Is acupuncture covered by health insurance?
- Some health insurance policies cover acupuncture, but others don’t. Coverage is often limited based on the condition being treated.
- An analysis of data from the Medical Expenditure Panel Survey, a nationally representative U.S. survey, showed that the share of adult acupuncturist visits with any insurance coverage increased from 41.1 percent in 2010–2011 to 50.2 percent in 2018–2019.
- Medicare covers acupuncture only for the treatment of chronic low-back pain. Coverage began in 2020. Up to 12 acupuncture visits are covered, with an additional 8 visits available if the first 12 result in improvement. Medicaid coverage of acupuncture varies from state to state.
Do acupuncturists need to be licensed?
- Most states license acupuncturists, but the requirements for licensing vary from state to state. To find out more about licensing of acupuncturists and other complementary health practitioners, visit the NCCIH webpage Credentialing, Licensing, and Education.
NCCIH-Funded Research
NCCIH funds research to evaluate acupuncture’s effectiveness for various kinds of pain and other conditions and to further understand how the body responds to acupuncture and how acupuncture might work. Some recent NCCIH-supported studies involve:
- Evaluating the feasibility of using acupuncture in hospital emergency departments.
- Testing whether the effect of acupuncture on chronic low-back pain can be enhanced by combining it with transcranial direct current stimulation.
- Evaluating a portable acupuncture-based nerve stimulation treatment for anxiety disorders.
More To Consider
- Don’t use acupuncture to postpone seeing a health care provider about a health problem.
- Take charge of your health—talk with your health care providers about any complementary health approaches you use. Together, you can make shared, well-informed decisions.
For More Information
NCCIH Clearinghouse
The NCCIH Clearinghouse provides information on NCCIH and complementary and integrative health approaches, including publications and searches of Federal databases of scientific and medical literature. The Clearinghouse does not provide medical advice, treatment recommendations, or referrals to practitioners.
Toll-free in the U.S.: 1-888-644-6226
Telecommunications relay service (TRS): 7-1-1
Website: https://www.nccih.nih.gov
Email: info@nccih.nih.gov (link sends email)
Know the Science
NCCIH and the National Institutes of Health (NIH) provide tools to help you understand the basics and terminology of scientific research so you can make well-informed decisions about your health. Know the Science features a variety of materials, including interactive modules, quizzes, and videos, as well as links to informative content from Federal resources designed to help consumers make sense of health information.
Explaining How Research Works (NIH)
Know the Science: How To Make Sense of a Scientific Journal Article
PubMed®
A service of the National Library of Medicine, PubMed® contains publication information and (in most cases) brief summaries of articles from scientific and medical journals. For guidance from NCCIH on using PubMed, see How To Find Information About Complementary Health Approaches on PubMed.
Website: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/
NIH Clinical Research Trials and You
The National Institutes of Health (NIH) has created a website, NIH Clinical Research Trials and You, to help people learn about clinical trials, why they matter, and how to participate. The site includes questions and answers about clinical trials, guidance on how to find clinical trials through ClinicalTrials.gov and other resources, and stories about the personal experiences of clinical trial participants. Clinical trials are necessary to find better ways to prevent, diagnose, and treat diseases.
Website: https://www.nih.gov/health-information/nih-clinical-research-trials-you
Research Portfolio Online Reporting Tools Expenditures & Results (RePORTER)
RePORTER is a database of information on federally funded scientific and medical research projects being conducted at research institutions.
Website: https://reporter.nih.gov
Key References
- Befus D, Coeytaux RR, Goldstein KM, et al. Management of menopause symptoms with acupuncture: an umbrella systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine. 2018;24(4):314-323.
- Bleck R, Marquez E, Gold MA, et al. A scoping review of acupuncture insurance coverage in the United States. Acupuncture in Medicine. 2020;964528420964214.
- Briggs JP, Shurtleff D. Acupuncture and the complex connections between the mind and the body. JAMA. 2017;317(24):2489-2490.
- Brinkhaus B, Roll S, Jena S, et al. Acupuncture in patients with allergic asthma: a randomized pragmatic trial. Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine. 2017;23(4):268-277.
- Chan MWC, Wu XY, Wu JCY, et al. Safety of acupuncture: overview of systematic reviews. Scientific Reports. 2017;7(1):3369.
- Coyle ME, Stupans I, Abdel-Nour K, et al. Acupuncture versus placebo acupuncture for in vitro fertilisation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Acupuncture in Medicine. 2021;39(1):20-29.
- Hershman DL, Unger JM, Greenlee H, et al. Effect of acupuncture vs sham acupuncture or waitlist control on joint pain related to aromatase inhibitors among women with early-stage breast cancer: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2018;320(2):167-176.
- Linde K, Allais G, Brinkhaus B, et al. Acupuncture for the prevention of episodic migraine. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2016;(6):CD001218. Accessed at cochranelibrary.com on February 12, 2021.
- Linde K, Allais G, Brinkhaus B, et al. Acupuncture for the prevention of tension-type headache. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2016;(4):CD007587. Accessed at cochranelibrary.com on February 12, 2021.
- MacPherson H, Vertosick EA, Foster NE, et al. The persistence of the effects of acupuncture after a course of treatment: a meta-analysis of patients with chronic pain. Pain. 2017;158(5):784-793.
- Qaseem A, Wilt TJ, McLean RM, et al. Noninvasive treatments for acute, subacute, and chronic low back pain: a clinical practice guideline from the American College of Physicians. Annals of Internal Medicine. 2017;166(7):514-530.
- Seidman MD, Gurgel RK, Lin SY, et al. Clinical practice guideline: allergic rhinitis. Otolaryngology—Head and Neck Surgery. 2015;152(suppl 1):S1-S43.
- Vickers AJ, Vertosick EA, Lewith G, et al. Acupuncture for chronic pain: update of an individual patient data meta-analysis. The Journal of Pain. 2018;19(5):455-474.
- White AR, Rampes H, Liu JP, et al. Acupuncture and related interventions for smoking cessation. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2014;(1):CD000009. Accessed at cochranelibrary.com on February 17, 2021.
- Zia FZ, Olaku O, Bao T, et al. The National Cancer Institute’s conference on acupuncture for symptom management in oncology: state of the science, evidence, and research gaps. Journal of the National Cancer Institute. Monographs. 2017;2017(52):lgx005.
Other References
- Adams D, Cheng F, Jou H, et al. The safety of pediatric acupuncture: a systematic review. Pediatrics. 2011;128(6):e1575-1587.
- Candon M, Nielsen A, Dusek JA. Trends in insurance coverage for acupuncture, 2010-2019. JAMA Network Open. 2022;5(1):e2142509.
- Cao J, Tu Y, Orr SP, et al. Analgesic effects evoked by real and imagined acupuncture: a neuroimaging study. Cerebral Cortex. 2019;29(8):3220-3231.
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Decision Memo for Acupuncture for Chronic Low Back Pain (CAG-00452N). Accessed at https://www.cms.gov/medicare-coverage-database/details/nca-decision-memo.aspx?NCAId=295 on June 25, 2021.
- Chen L, Lin C-C, Huang T-W, et al. Effect of acupuncture on aromatase inhibitor-induced arthralgia in patients with breast cancer: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. The Breast. 2017;33:132-138.
- Choi G-H, Wieland LS, Lee H, et al. Acupuncture and related interventions for the treatment of symptoms associated with carpal tunnel syndrome. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2018;(12):CD011215. Accessed at cochranelibrary.com on January 28, 2021.
- Cui J, Wang S, Ren J, et al. Use of acupuncture in the USA: changes over a decade (2002–2012). Acupuncture in Medicine. 2017;35(3):200-207.
- Federman DG, Zeliadt SB, Thomas ER, et al. Battlefield acupuncture in the Veterans Health Administration: effectiveness in individual and group settings for pain and pain comorbidities. Medical Acupuncture. 2018;30(5):273-278.
- Feng S, Han M, Fan Y, et al. Acupuncture for the treatment of allergic rhinitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. American Journal of Rhinology & Allergy. 2015;29(1):57-62.
- Franco JV, Turk T, Jung JH, et al. Non-pharmacological interventions for treating chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2018;(5):CD012551. Accessed at cochranelibrary.com on January 28, 2021.
- Freeman MP, Fava M, Lake J, et al. Complementary and alternative medicine in major depressive disorder: the American Psychiatric Association task force report. The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry. 2010;71(6):669-681.
- Giovanardi CM, Cinquini M, Aguggia M, et al. Acupuncture vs. pharmacological prophylaxis of migraine: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Frontiers in Neurology. 2020;11:576272.
- Hu C, Zhang H, Wu W, et al. Acupuncture for pain management in cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2016;2016;1720239.
- Jiang C, Jiang L, Qin Q. Conventional treatments plus acupuncture for asthma in adults and adolescent: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2019;2019:9580670.
- Ji M, Wang X, Chen M, et al. The efficacy of acupuncture for the treatment of sciatica: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2015;2015:192808.
- Kaptchuk TJ. Acupuncture: theory, efficacy, and practice. Annals of Internal Medicine. 2002;136(5):374-383.
- Kolasinski SL, Neogi T, Hochberg MC, et al. 2019 American College of Rheumatology/Arthritis Foundation guideline for the management of osteoarthritis of the hand, hip, and knee. Arthritis Care & Research. 2020;72(2):149-162.
- Langevin H. Fascia mobility, proprioception, and myofascial pain. Life. 2021;11(7):668.
- Liu Z, Liu Y, Xu H, et al. Effect of electroacupuncture on urinary leakage among women with stress urinary incontinence: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2017;317(24):2493-2501.
- MacPherson H, Hammerschlag R, Coeytaux RR, et al. Unanticipated insights into biomedicine from the study of acupuncture. Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine. 2016;22(2):101-107.
- Maeda Y, Kim H, Kettner N, et al. Rewiring the primary somatosensory cortex in carpal tunnel syndrome with acupuncture. Brain. 2017;140(4):914-927.
- Manheimer E, Cheng K, Wieland LS, et al. Acupuncture for hip osteoarthritis. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2018;(5):CD013010. Accessed at cochranelibrary.com on February 17, 2021.
- Moura CC, Chaves ECL, Cardoso ACLR, et al. Auricular acupuncture for chronic back pain in adults: a systematic review and metanalysis. Revista da Escola de Enfermagem da U S P. 2019;53:e03461.
- Napadow V. Neuroimaging somatosensory and therapeutic alliance mechanisms supporting acupuncture. Medical Acupuncture. 2020;32(6):400-402.
- Patnode CD, Henderson JT, Coppola EL, et al. Interventions for tobacco cessation in adults, including pregnant persons: updated evidence report and systematic review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2021;325(3):280-298.
- Qin Z, Liu X, Wu J, et al. Effectiveness of acupuncture for treating sciatica: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2015;2015;425108.
- Smith CA, Armour M, Lee MS, et al. Acupuncture for depression. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. 2018;(3):CD004046. Accessed at cochranelibrary.com on January 20, 2021.
- US Preventive Services Task Force. Interventions for tobacco smoking cessation in adults, including pregnant persons. US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. JAMA. 2021;325(3):265-279.
- Vase L, Baram S, Takakura N, et al. Specifying the nonspecific components of acupuncture analgesia. Pain. 2013;154(9):1659-1667.
- Wang R, Li X, Zhou S, et al. Manual acupuncture for myofascial pain syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Acupuncture in Medicine. 2017;35(4):241-250.
- World Health Organization. WHO Traditional Medicine Strategy: 2014–2023. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization, 2013. Accessed at https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241506096 on February 2, 2021.
- Wu M-S, Chen K-H, Chen I-F, et al. The efficacy of acupuncture in post-operative pain management: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2016;11(3):e0150367.
- Xu S, Wang L, Cooper E, et al. Adverse events of acupuncture: a systematic review of case reports. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2013;2013:581203.
- Yang J, Ganesh R, Wu Q, et al. Battlefield acupuncture for adult pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. The American Journal of Chinese Medicine. 2021;49(1):25-40.
- Yang Y, Wen J, Hong J. The effects of auricular therapy for cancer pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2020;2020:1618767.
- Yeh CH, Morone NE, Chien L-C, et al. Auricular point acupressure to manage chronic low back pain in older adults: a randomized controlled pilot study. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine. 2014;2014;375173.
- You F, Ruan L, Zeng L, et al. Efficacy and safety of acupuncture for the treatment of oligoasthenozoospermia: a systematic review. Andrologia. 2020;52(1):e13415.
- Zhang X-C, Chen H, Xu W-T, et al. Acupuncture therapy for fibromyalgia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Journal of Pain Research. 2019;12:527-542.
- Zheng H, Chen R, Zhao X, et al. Comparison between the effects of acupuncture relative to other controls on irritable bowel syndrome: a meta-analysis. Pain Research and Management. 2019;2019:2871505.
Acknowledgments
NCCIH thanks Pete Murray, Ph.D., David Shurtleff, Ph.D., and Helene M. Langevin, M.D., NCCIH for their review of the 2022 update of this fact sheet.
This publication is not copyrighted and is in the public domain. Duplication is encouraged.
NCCIH has provided this material for your information. It is not intended to substitute for the medical expertise and advice of your health care provider(s). We encourage you to discuss any decisions about treatment or care with your health care provider. The mention of any product, service, or therapy is not an endorsement by NCCIH.